- Have any questions?
- info@cuttingedge.com.pk
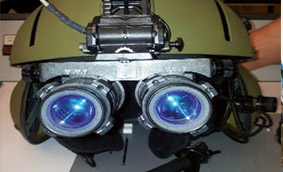
NVDs Night vision devices
A Night Vision Device (NVD), also known as Night Optical / Observation Device (NOD) and Night Vision Goggles (NVG), is an optoelectronic device that allows images to be produced in light levels that approach total obscurity. The image may be a conversion to visible light of both visible light and near-infrared, while thermal imaging is denoted by convention detection of thermal infrarot. Typically the image produced is monochrome, for example shades of green. The military and law enforcement agencies most frequently use NVDs, but are available to civilian users. Usually, the term refers to a complete unit, including an intensifier tube, a protective and generally water-resistant housing And some kind of mounted system. Many NVDs also have optical components such as a lens for sacrifice Or mirror or telescopic lenses. An NVD may have an IR illuminator which makes it an active system, as opposed to a passive night vision.Night-vision devices were first used in the Second World War and used extensively during the Vietnam War.After their launch, the technology has evolved considerably, resulting in several "generations" of night-vision equipment with improvements in efficiency and price reductions. As a result, they are available for a wide range of applications, including gunners, drivers and aviators, for example.